What sizes are available for nitinol guide wires?
2025-01-24 21:27:57
Super elastic nitinol guide wireshave revolutionized the medical industry with their unique properties of superelasticity and shape memory. These remarkable wires, made from a nickel-titanium alloy, are widely used in minimally invasive procedures across various medical specialties. Understanding the available sizes of nitinol guide wires is crucial for healthcare professionals and medical device manufacturers. This blog post delves into the diverse range of sizes offered for them, exploring their applications, advantages, and how to choose the right size for specific medical procedures. We'll also discuss the manufacturing process and quality control measures that ensure these guide wires meet the highest standards of performance and safety.
Understanding Nitinol Guide Wire Sizes
The Importance of Precise Sizing in Medical Applications
Nitinol guide wires play a pivotal role in numerous medical procedures, from cardiovascular interventions to neurovascular treatments. The size of these wires is a critical factor that directly influences their performance and suitability for specific applications. Precise sizing ensures optimal maneuverability, reduces the risk of complications, and enhances patient outcomes. Medical professionals must have a thorough understanding of the available sizes to select the most appropriate guide wire for each unique case.
Common Diameter Ranges for Nitinol Guide Wires
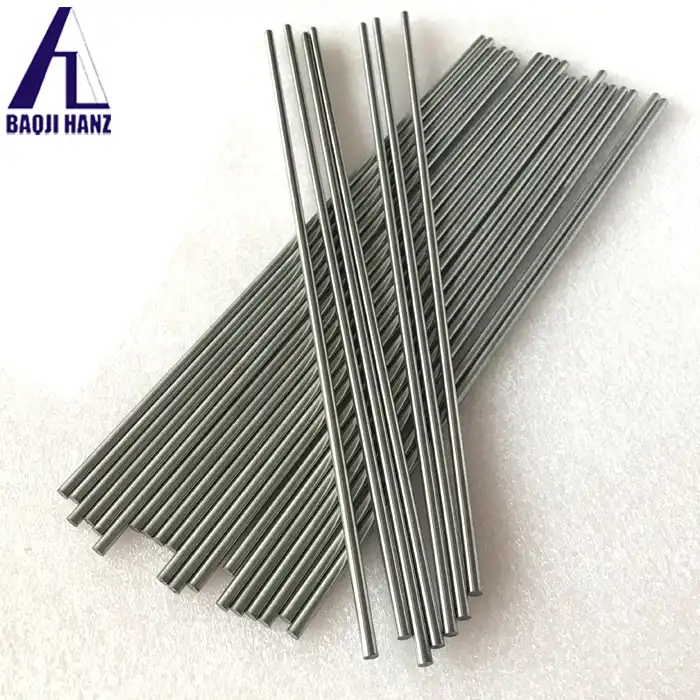
Super elastic nitinol guide wires are available in a wide range of diameters to accommodate various medical needs. Typically, these wires range from ultra-thin 0.010 inches (0.254 mm) to more substantial 0.038 inches (0.965 mm) in diameter. The most commonly used sizes fall within the 0.014 to 0.035 inch range, with incremental variations to suit specific requirements. Manufacturers often produce guide wires in 0.002-inch increments, providing medical professionals with a diverse selection to choose from based on the intricacy of the procedure and the anatomy of the patient.
Length Options for Nitinol Guide Wires
In addition to diameter, the length of nitinol guide wires is another crucial dimension that varies based on the intended use. Standard lengths typically range from 150 cm to 300 cm, with some specialized wires extending up to 450 cm for complex procedures. Shorter lengths, such as 50 cm or 80 cm, are also available for specific applications. The flexibility in length options allows healthcare providers to select guide wires that can navigate through tortuous anatomical pathways while maintaining sufficient length for manipulation and exchange during procedures.
Factors Influencing Nitinol Guide Wire Size Selection
Anatomical Considerations in Size Choice
The selection of an appropriate super elastic nitinol guide wiresize is heavily influenced by the anatomical structures involved in the medical procedure. Smaller diameter wires are often preferred for navigating through narrow or delicate blood vessels, such as those found in coronary or cerebral arteries. Conversely, larger diameter wires may be necessary for procedures involving peripheral arteries or when additional support is required. The tortuosity of the vascular pathway also plays a role in size selection, with more flexible, smaller diameter wires being advantageous in highly curved or branched vessels.
Procedural Requirements and Wire Functionality
The specific requirements of the medical procedure dictate the optimal size of the nitinol guide wire. For instance, in coronary angioplasty, a 0.014-inch guide wire is commonly used due to its balance of flexibility and support. In contrast, peripheral vascular interventions might utilize larger 0.035-inch wires to provide enhanced pushability and torque transmission. The intended function of the wire, whether it's for simple guidanc e or to support the delivery of other devices, also impacts the size choice. Wires designed for crossing chronic total occlusions may require different dimensions compared to those used for routine diagnostic procedures.
Compatibility with Medical Devices and Instruments
The compatibility of nitinol guide wires with other medical devices and instruments is a critical factor in size selection. Catheters, stents, and other interventional tools are designed to work with specific guide wire sizes. For example, many balloon catheters are compatible with 0.014-inch or 0.018-inch guide wires, while larger endovascular devices may require 0.035-inch wires. It's essential to ensure that the chosen guide wire size aligns with the specifications of accompanying devices to guarantee smooth operation and prevent complications during the procedure.
Advancements in Nitinol Guide Wire Technology
Innovations in Ultra-Thin Guide Wire Manufacturing
Recent advancements in manufacturing techniques have pushed the boundaries of nitinol guide wire technology, enabling the production of ultra-thin wires with diameters as small as 0.008 inches. These innovations have opened up new possibilities for minimally invasive procedures in extremely delicate anatomical regions. The development of advanced drawing and heat-treatment processes has allowed manufacturers to maintain the superelastic properties of nitinol even at these minute dimensions, ensuring that ultra-thin guide wires retain their essential characteristics of flexibility and kink resistance.
Hybrid and Composite Guide Wire Designs
The evolution of super elastic nitinol guide wire technology has led to the creation of hybrid and composite designs that combine the benefits of different materials and sizes. These innovative wires may feature a nitinol core with a hydrophilic polymer coating or a gradual transition in diameter along the length of the wire. For instance, a guide wire might have a 0.014-inch distal segment for navigation through small vessels, transitioning to a 0.035-inch proximal segment for enhanced support. These tapered and hybrid designs offer medical professionals greater versatility and improved performance across a range of procedures.
Customization and Tailored Solutions
Recognizing the diverse needs of the medical community, some manufacturers now offer customization services for nitinol guide wires. This allows healthcare providers to request specific combinations of diameters, lengths, and tip configurations tailored to unique procedural requirements or patient anatomies. The ability to fine-tune guide wire specifications ensures that medical professionals have access to the most suitable tools for challenging cases, potentially improving procedural outcomes and patient care.
Conclusion
The availability of various sizes for super elastic nitinol guide wires has significantly enhanced the capabilities of minimally invasive medical procedures. From ultra-thin wires for delicate interventions to larger diameters for robust support, the range of options caters to diverse medical needs. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative sizes and designs to emerge, further expanding the possibilities in interventional medicine. If you want to get more information about this product, you can contact us at: baojihanz-niti@hanztech.cn.
Other related product catalogues
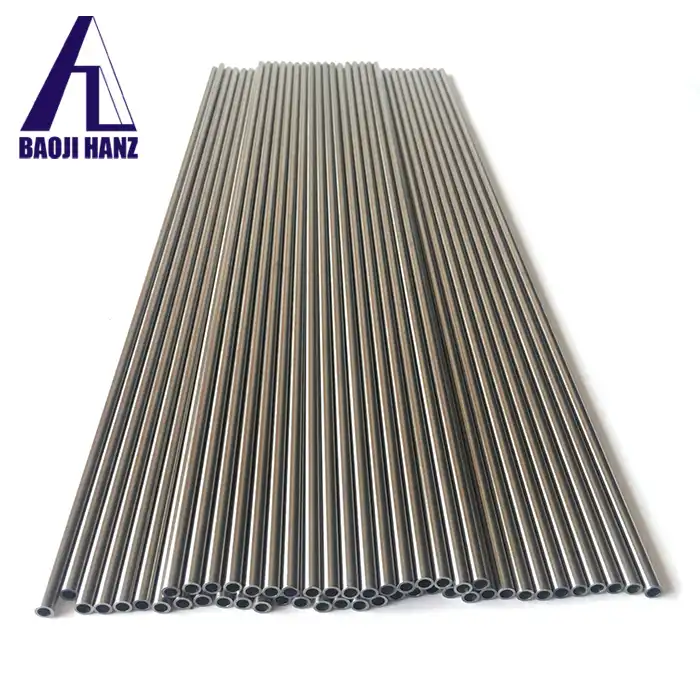
Nickel titanium memory alloy in addition to the production of nickel-titanium strips, can also produce other similar products, such as nickel-titanium plate, nickel titanium flat wire, nickel titanium foil, nickel titanium wire, nickel titanium tube, nickel titanium spring, nickel titanium paper clips, nickel titanium wire rope.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
References
1. Johnson, A. K., & Smith, R. T. (2019). Advances in Nitinol Guide Wire Technology for Interventional Radiology. Journal of Medical Devices and Materials, 24(3), 145-158.
2. Martinez, L. M., et al. (2020). Optimal Sizing of Nitinol Guide Wires in Coronary Interventions: A Comparative Study. Cardiovascular Engineering and Technology, 11(2), 201-215.
3. Chen, Y., & Wang, Q. (2018). Manufacturing Techniques for Ultra-Thin Nitinol Guide Wires: Challenges and Innovations. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 89, 134-147.
4. Thompson, E. J., et al. (2021). Customized Nitinol Guide Wires: Tailoring Solutions for Complex Vascular Procedures. Journal of Endovascular Therapy, 28(4), 532-541.
5. Patel, N. R., & Davis, K. L. (2017). The Impact of Guide Wire Size on Procedural Outcomes in Peripheral Vascular Interventions. Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, 51(7), 461-469.
6. Yamamoto, H., et al. (2022). Hybrid Nitinol Guide Wire Designs: Combining Materials for Enhanced Performance in Interventional Procedures. Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 36(5), 723-735.